Worked example
Which sets of orbitals are filled and which sets are partially filled in the following neutral atoms (a) Al (b) Cl (c) V (d) As (e) Kr?
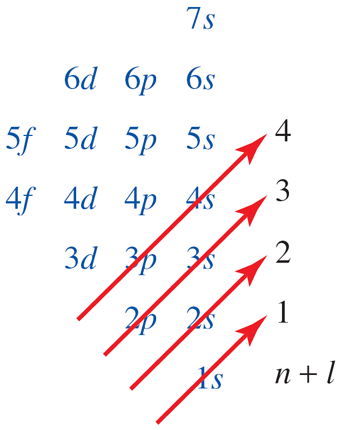
Recall from above that s orbitals can accommodate a maximum of 2 electrons, p orbitals 6 electrons, d orbitals 10 electrons, and f orbitals 14 electrons. Therefore, knowing the atomic number of the elements allows us to write the electron configurations.
- Al : Z = 13 : 1s full (2), 2s full (2), 2p full (6), 3s full (2), 3p partially full (1).
- Cl : Z = 17 : 1s full (2), 2s full (2), 2p full (6), 3s full (2), 3p partially full (5).
- V : Z = 23 : 1s full (2), 2s full (2), 2p full (6), 3s full (2), 3p full (6), 4s full (2), 3d partially full (3).
- As : Z = 33 : 1s full (2), 2s full (2), 2p full (6), 3s full (2), 3p full (6), 4s full (2), 3d full (10), 4p partially full (3).
- Kr : Z = 36 : 1s full (2), 2s full (2), 2p full (6), 3s full (2), 3p full (6), 4s full (2), 3d full (10), 4p full (6)
[Note, that all shells and sub-shells are full, which is characteristic of Group 18 elements.]