Structure of the periodic table
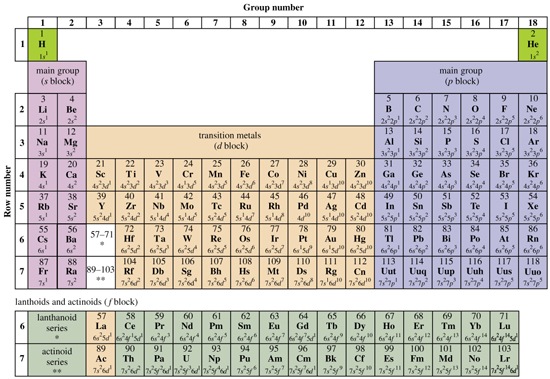
The distribution of electrons in atoms is known as the atom's 'electronic structure' or 'electron configuration' and the guiding principles for interpreting electron configurations are the Pauli exclusion principle (no two electrons in atoms can have the same values of all 4 quantum numbers) and Hund's rule (the lowest energy configuration involving orbitals of equal energies is the one with the maximum number of electrons with the same spin orientation). The lowest energy state of electrons in atoms is known as the 'ground state' and is the most stable electronic state.