Order of orbital filling
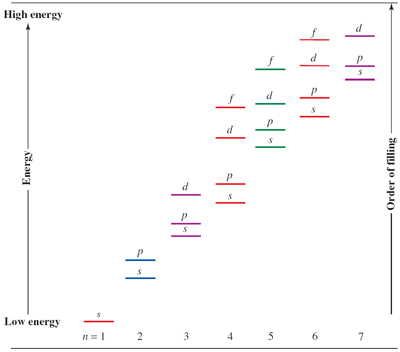
The ground state electronic configuration is constructed in accordance with the Aufbau principle which states that electrons are assigned to orbitals in the following order: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p etc. The filling of s, p, d and f orbitals give rise to the 's block', 'p block', 'd block' and 'f block' elements in Groups 1–2, 13–18, 3–12 and the lanthanoid and actinoid elements, respectively. The number of elements in each period results from the above order of orbital filling.
Electrons in atoms are classified as 'core' or 'valence' electrons. The valence electrons determine the chemical properties of an element and are the outermost electrons – i.e. those in the highest energy orbitals. Core electrons are not easily removed from atoms and therefore do not participate in chemical reactions.