Atomic radii
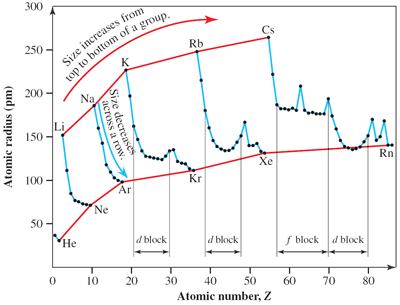
In general, atomic radii decrease across a period and increase down a group of the periodic table. For example, for Period 3, the atomic radius of the sodium atom is 186 pm and that of the argon atom is 97 pm and for Group 1, the atomic radius of the lithium atom is 152 pm and that of the caesium atom is 265 pm.
Exceptions again occur for transition elements, lanthanoids and actinoids; atomic radii also decrease in each series but the trend is not regular due to irregular shielding by the added d or f electrons. For example, the atomic radius of the scandium atom is 160 pm and that of zinc is 140 pm but that of nickel is 132 pm. In general, the relative atomic size changes across d and f blocks are less than those across s and p blocks.