Ionisation energy
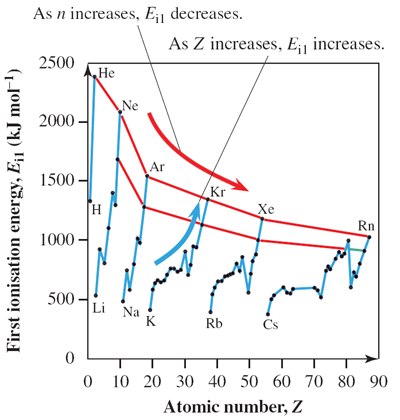
Ionisation energy (Ei) is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom. Ionisation energy increases across a period and decreases down a group. For example, for Period 3, Ei (Na) is 496 kJ mol–1 and Ei (Ar) is 1520 kJ mol–1, respectively. For Group 18, Ei (He) is 2372 kJ mol–1 and Ei (Rn) is 1037 kJ mol–1, respectively. Ionisation energies for transition elements increase moderately within a series but the increase is not regular. For example, Ei (Mn) is 717 kJ mol–1, Ei (Fe) is 763 kJ mol–1, Ei (Co) is 758 kJ mol–1 and Ei (Ni) is 737 kJ mol–1, respectively.